Regular STD testing is crucial for maintaining sexual health and preventing the spread of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Understanding how often you should get tested can help ensure timely diagnosis and treatment, reducing the risk of complications and transmission to others. This article provides guidelines on the frequency of STD testing based on various factors and scenarios.
General Recommendations for STD Testing
The frequency of STD testing can vary depending on individual risk factors, sexual behavior, and health status. Here are some general recommendations:
- Annual Testing:For sexually active individuals who are at average risk, getting an STD test once a year is generally recommended. This helps ensure that any infections are detected early and managed appropriately.
- Increased Frequency for High-Risk Groups:Individuals with higher risk factors should consider more frequent testing. High-risk factors include multiple sexual partners, inconsistent condom use, and engaging in high-risk sexual practices.
Factors Influencing Testing Frequency
Several factors can influence how often you should get tested for STDs. These include:
- New Sexual Partners:If you have a new sexual partner, it is advisable to get tested before engaging in unprotected sex. This helps prevent the transmission of STDs and ensures that both partners are aware of their sexual health status.
- Symptoms of STDs:If you experience symptoms such as unusual discharge, sores, itching, or pain during urination, it is important to get tested promptly, regardless of your last testing date. Symptoms may indicate an active infection that requires immediate treatment.
- Known Exposure:If you have had a known exposure to an STD, such as unprotected sex with someone diagnosed with an infection, getting tested as soon as possible is essential. Some infections might not show symptoms immediately, so timely testing can prevent further spread.
Testing Recommendations for Specific Groups
Certain groups may have specific testing recommendations based on their health and lifestyle:
- Pregnant Women:Pregnant women should get tested for STDs early in their pregnancy and again later as recommended by their healthcare provider. STDs can affect both the mother and the baby, making regular testing crucial for ensuring a healthy pregnancy.
- Individuals with Multiple Partners:Those with multiple sexual partners should get tested more frequently, such as every 3 to 6 months. This helps manage and monitor sexual health in high-risk situations.
- People with Chronic Conditions:Individuals with chronic conditions such as HIV should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for regular STD testing. This ensures comprehensive management of their overall health and any associated infections.
Types of STD Tests and What They Involve
Understanding the types of STD tests and what they involve can help you feel more comfortable with the testing process:
- Urine Tests:Often used to detect chlamydia and gonorrhea, urine tests are non-invasive and require only a urine sample.
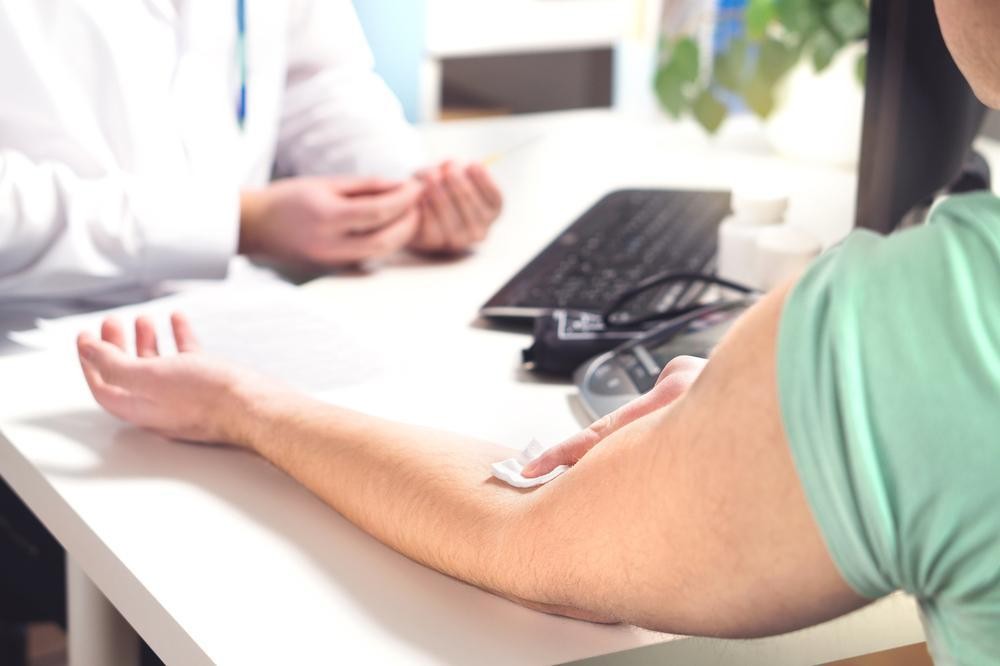
- Blood Tests:These tests can detect infections such as HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis. A blood sample is required, usually drawn from a vein in your arm.
- Swabs:For some STDs, such as herpes and trichomoniasis, swabs may be taken from sores, discharge, or other affected areas.
Conclusion
Regular STD testing is a vital component of sexual health and well-being. By understanding how often you should get tested and the factors that influence testing frequency, you can take proactive steps to protect yourself and your partners.
Whether you have new sexual partners, experience symptoms, or fall into high-risk categories, timely testing ensures early detection and effective management of STDs. Make STD testing a regular part of your health routine to stay informed and healthy.