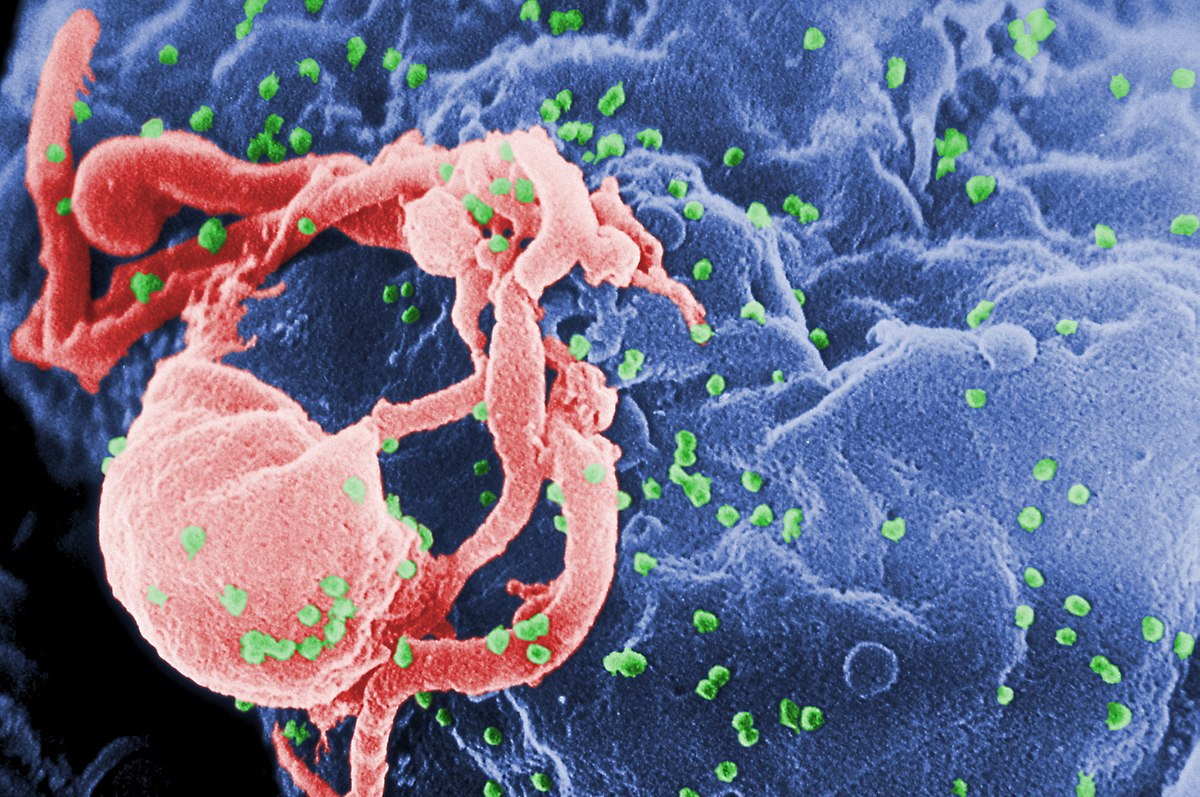
An HIV infection (HIV) attacks the body’s immune system. It is a virus that attacks the immune system, CD4 cells, which are white blood cells. HIV destroys CD4 cells, lowering a people’s immunity to secondary infections including tuberculosis and yeast infections, as well as dangerous bacterial infections and cancers. (HIV) produces the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which reduces the body’s capacity to fight infections. HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a virus that causes The virus to be spread by interaction with contaminated blood, sperm, and vaginal fluids. Chills, dry lips, and tiredness are flu-like symptoms that might emerge several weeks after HIV infection. The illness is usually asymptomatic until it progresses to AIDS. Fat boy fitman store provides medicine at cheap market price.
What exactly is HIV?
virus symbol
Attacks cells in the immune system that attacks the body’s immune system. If the human immunodeficiency virus is not treated, AIDS can develop
There is presently no viable treatment available. People who contract HIV are infected for life.
HIV, on the other hand, maybe managed with good medical treatment. Sufferers who get appropriate HIV therapy can live long and healthy lives while protecting their relationships.
Where did HIV originate?
HIV infection history
In Central Africa, a kind of chimp caused HIV/aids in people.
When humans hunted these apes for meat and came into touch with their tainted blood, the chimpanzee virus (named immunodeficiency virus (SIV) was most likely transmitted to humans. HIV may have been transmitted from chimps to humans as early as the 1800s, according to a study. Over decades, HIV spread slowly across Africa and then into other parts of the world. Since the mid-1970s, the virus has been present in the United States.
How can I tell if I have AIDS?
The one and the only way to find out if you have Aids is to be tested. Knowing your HIV status allows you to make informed decisions to avoid contracting or transmitting HIV.
Are there any signs?
Graph depicting HIV symptoms: Cold, rashes, excessive sweating, muscle pains, sinus infection, tiredness, swollen glands, and mouth ulcers are all symptoms of HIV.
After being infected, a few people get flu-like symptoms.
These symptoms might persist anywhere from a few days to a few weeks. Fever, chills, rash, night sweats, muscular aches, sore throat, exhaustion, swollen glands, and mouth ulcers are just some of the symptoms of the flu.
However, many people do not feel ill throughout an acute HIV infection.
What are the HIV stages?
When HIV patients do not get therapy, they normally move through three phases. However, HIV medication can halt or stop the growth of the illness. With treatment advances, advancement to Phase three is less prevalent now than it was in the early stages of HIV.
- Acute HIV infection
- HIV Infection Is Chronic
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)